“The big domino” refers to the task that, once completed, eliminates a number of other challenges along with it. My goal in writing this is to help you identify and topple the big domino in your business so your business can evolve to the next stage of growth.
I’ll start by outlining a unique 2-step business development strategy. Then, I’ll provide a series of high-yield, actionable specifics that address all major aspects of business development.
The 2-Step Business Development Process
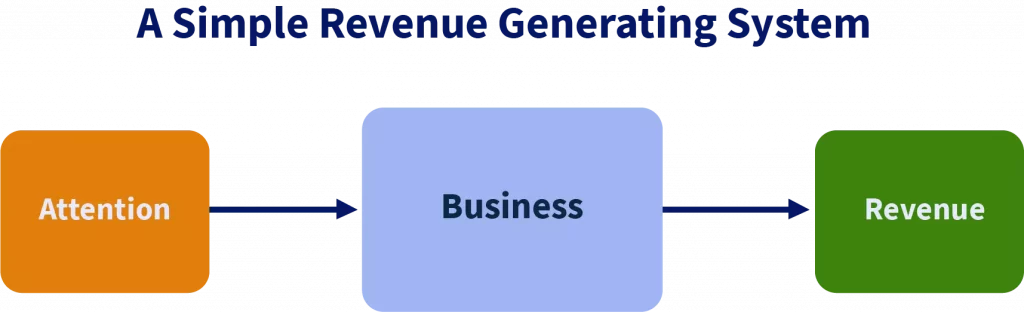
At its core, your business is a revenue generation system. The system takes your prospect’s attention, creates a paying customer, delivers value, and outputs revenue.
A business developer has high level goals that address the overall performance of this system: They should be working on the system, as opposed to in it.
All systems, both simple and complex, are limited by one main constraint.* And when this constraint is relieved output increases. Your business growth strategy should center around identifying and relieving the main constraint. By doing this, other problems self-resolve, important matters become irrelevant, and difficult challenges become more manageable.
*The “theory of constraints” is adapted from “The Goal” by Eli Goldratt.
1. Find The Weakest Link
Start by deconstructing your business’ operations into its constituent processes and sub-processes. Your goal is to find the weakest link. Use KPIs (key performance indicators) to analyze the system’s components and identify the constraint.
Here are some sources of constraint commonly encountered by professional services firms – and important associated KPIs.
| Constraint Type | Associated KPIs |
|---|---|
| Profitability constraints | Low operating margin Low customer lifetime value |
| Customer acquisition constraints | Low customer volume High customer acquisition costs |
| Lead Generation constraints | High cost per lead Low Lead Volume |
| Sales process constraints | Low contact rate Low Close rate |
| Operational constraints | High Labor Costs Low Customer Experience Scores (NPS, CSAT, CES) |
| Market constraints | Slowing growth rate Decreasing profitability |
You need to get a keen sense of what your performance metrics should be – and what they could be. Large performance deficits often point to the main constraint.
If you need help getting oriented, you should be able to find industry medians and ranges to use as benchmarks. It’s also fine to examine performance ranges in other industries with similar dynamics – you’ll be surprised how stable KPIs can be from one industry to another.
You need to get a keen sense of what your performance metrics should be – and what they could be. Large performance deficits often point to the main constraint.
If you need help getting oriented, you should be able to find industry medians and ranges to use as benchmarks. It’s also fine to examine performance ranges in other industries with similar dynamics – you’ll be surprised how stable KPIs can be from one industry to another.
Ideas for finding industry benchmark data:
- Google searches: average [KPI] + for [industry]
- Ask other business owners
- Evaluate competitors
- Read industry reports
- Request financials from businesses that are for sale
2. Find and Test Ideas
Create a business development plan with ideas for relieving the constraint. An idea can be anything from a sophisticated new sales strategy to a new set of strategic partnerships.
Nothing you try is guaranteed to work: all of your options are just ideas that you test. The more ideas you have access to, the better your chances of finding an innovative, low-risk solution.
1. Brainstorm
Think deeply and honestly about the main constraint and your options for relieving it. Theorize about what it takes to perform in the top range of your industry, and think up of ways to get yourself there. Force yourself to come up with a list of 5-10 unique ideas. You might be surprised by your creative capacity after an hour or two of deep thought.
2. Research
Consume information and consult with experts with the sole purpose of finding ideas to relieve the constraint.
3. Emulate
Consider emulating your most successful competitors: reverse engineer their success by monitoring their business practices. Look for principles and ideas that you can extract for use in your own business.
4. Test
When you’re done strategizing, your growth plan should consist of a set of actionable ideas for relieving the main constraint. Begin by testing the lowest risk, highest reward ideas. Keep testing ideas until the constraint is relieved. Once the constraint is relieved, move on and address the next constraint instead of sticking around and over-optimizing.
Principles of Idea Testing
1. Everything is a test
Your business is a system with a set of variables that work synergistically towards the singular goal of outputting revenue. Everything you do outside of regular operations is a test change to the system.
2. Be Scientific
Have a theory underlying all of your tests. Prove or disprove the theory with each test, and allow your framework of principles to evolve accordingly. This way, everything you do is a win: “failed” tests yield lessons and successful tests yield growth.
3. Test One Variable at a Time
It’s nearly impossible to determine test outcomes when you have more than one variable.
4. Have a Verifiable Outcome
You need to understand exactly what you’re looking for to qualify a test as “successful” or “unsuccessful.”
5. Be Patient
It can take time for your idea to start working so don’t give up until you’ve given things a proper chance.
6. Be Persistent
Business growth isn’t a linear process – A lot of trial and error is involved. Persistence is required to unlock the next stage of growth. If one test doesn’t work, take the lesson on board and keep trying other things.
7. Embrace Core Principles
Get the basics right before you get fancy, especially if you’re underperforming.
8. Embrace New Ideas
Never stop taking small calculated risks on new ideas – this is the only way to prevent inertia and achieve peak performance.
6 Ways To Increase Profitability
If your operating margins need work, here are some strategic initiatives to directly address profitability.
1. Develop a high-performance website
A website has immense potential to increase profitability. Almost every potential customer will look up your website before becoming a new customer. Most businesses are nowhere near utilizing the full potential of their website. Good web design and sales copy can be powerful sales tools. And through SEO content marketing you can build a massive customer base.
2. Increase customer lifetime value
- What other products, services, and subscriptions can you offer existing customers with relative ease?
- Could your existing customers benefit from any affiliate program or white-label offers?
- Are there potential strategic partners that provide products/services your customers would be interested in? Can you send your clients to them for a commission?
- Can you ascend your main offer for high-paying clients by charging a premium price point for a more bespoke, “done-for-you” style service?
3. Optimize Pricing
For every market and product, there’s a pricing sweet spot where profit is maximized.
Test higher price points and see if you can increase profitability without demand dropping off significantly. The industry standard is rarely the best price point, so you need to explore this yourself.
4. Reassess Your Customer Avatar
A deep understanding of your customer enhances every aspect of your business. Enhance your understanding of who they are, their pain points, their problems, and their beliefs. Understand their desires and learn to speak their language. Use this renewed understanding to optimize your lead generation, sales processes, and strategic planning.
5. Niche-down
You can often increase profitability (at the cost of scalability) by tailoring your efforts towards a specific sub-market. This is highly effective when that niche has specific problems that aren’t directly addressed by the main market.
- Niching down can justify higher prices
- Niching can decrease customer acquisition costs: Machine learning ad platforms like Facebook have made marketing to a narrow target audience highly cost-effective.
- Niching down also often decreases service delivery costs by reducing your client variety
6. Build Your Brand
Branding is a powerful ROI multiplier – a prospect is far more likely to patronize, remember, and recommend a business with memorable branding. Brand development is an ongoing process so get into the habit of thinking deeply about your brand, and continually find ways to develop it.
Supercharge Your Customer Acquisition
Your customer acquisition system is how your business captures and converts attention into a paying customer. High customer acquisition costs could have a number of causes so you need to examine your customer acquisition system carefully.
Customer acquisition is best divided into two categories
Lead generation system
Sales Process
Lead Generation: Optimize and Diversify
Your lead generation system is how you generate demand for your business. If your lead costs are high, consider testing different outsourced customer acquisition agencies. If your online presence is established, consider building out a robust, in-house lead generation funnel.
If you have a low lead volume, add new lead sources. Even if your lead volume is fine, you should try your best to diversify your lead sources.
Referral Systems
If you’re one of the millions of businesses that relies on referrals, note that you will almost certainly require additional lead generation systems to grow.
Here’s a low-risk way to optimize your referral ecosystem
- Create a referral expectation: Inform new customers that your business relies on referrals.
- First request feedback: Before asking for a referral, ask for feedback on their client experience. If it was good, then ask for a referral.
- Give specific instruction: Instead of asking for a referral, consider giving them a simple actionable task – like an email template they can send to 5 people.
Type 1 Joint Venture
This is a type of strategic partnership where you leverage the resources of another business to improve your customer acquisition strategies. Approach businesses with a similar, non competing customer base and offer them referrals – or a commission – in exchange for one of the following:
- Referrals: they offer their customers a special discount for patronizing your business
- Leads: refer leads that aren’t a good fit for them to you
- List sharing: access to their customer list for marketing purposes (beware of privacy laws)
Lead Purchasing
There are many companies that specialize in generating leads for various industries. Consider trialing a few of these agencies. I’ve seen a number of companies scale up their operations on the back of purchased leads.
Cold Email outreach
This is not to be confused with email marketing (sending marketing emails to a subscriber list). Cold outreach is good for B2B sales and testing different offers. Cold email outreach pairs well with LinkedIn outreach, cold calling, and direct-mail to generate multiple touchpoints.
Content / SEO
Search engine optimized content marketing is a powerful way to build relevant website traffic by leveraging your knowledge. This is also a unique competitive advantage for small business owners because good content is hard to scale. Recently, Google has gotten very good at analyzing and promoting good content.
Digital advertising funnel
The number of ways you can optimize, expand, and improve your online funnels is nearly limitless. Build out your funnel one stage at a time, continually testing new things as you go (segmentations, re-targeting strategies, ad platforms, marketing hooks, ad creative, and copy).
Sales Tips
The most highly effective and evergreen sales format is called consultative selling, which centers around understanding your prospect’s problems/pain points and then prescribing your offer as the solution. This isn’t as much a ”tactic” as it is just understanding your customer and having the right solution. But it’s highly effective in focusing the client’s attention on the value your product or service brings.
Your sales process is the way in which you manage the inflow of leads and convert them to paying customers. Leads are a precious resource. And a robust sales system can drastically enhance your utilization of this resource.
High-Yield Sales Tips:
1. Increase contact speed
Studies have shown that connecting to a web-generated lead within 5 minutes increases contact rates by 900%.
2. Increase contact modalities
Engage leads in as many ways as possible (email, text messaging, phone calls, LinkedIn, etc.) to enhance contact rates and close rate.
3. Use software solutions
A CRM is crucial to systematize your efforts. Lead scoring and data enrichment tools are great later-stage sales process optimization tools
4. Have a sophisticated follow-up system
Have a specific plan for following up prospects that haven’t yet bought or declined (missed appointment, tire kickers, etc.)
Appointment Setting
If you have a low close rate, consider hiring a dedicated appointment setter to maximize the effectiveness of your sales team.
The role of an appointment setter:
- Manage multiple lead sources
- Qualify and nurture prospects
- Filter out non-buyers
- Answer questions
- Book appointments into your calendar
- Pre-frame sales call and establish expectations
- Send out reminders
- Follow up on missed appointments
- Obtain feedback and inquire about reasons for not purchasing
Operations: The Art of Keeping Up
New businesses face very serious operational constraints when day-to-day service delivery is reliant on their time. And once an owner has extracted themselves from a business, a series of staffing and management constraints will follow.
You may have heard of the Pareto Principle – or “80/20 rule.” This is the principle that posits that 20% of your effort produces 80% of your results. I’ve found this to be an effective paradigm for evaluating operations.
The Secret to Outstanding Customer Experience
When a business is said to have ‘grown too quickly,’ it’s because rapid growth is causing operational constraints and resulting in an unsatisfactory customer experience.
A new customer enters your business ecosystem with a certain expectation mostly based on what they learned during the sales phase. Deepen your understanding of this expectation and focus on maximizing their desired outcome. Double down on what works and consider eliminating work that customers don’t value.
80/20 Rule: “What 20% of our service delivery efforts bring in 80% of the customer’s desired result?”
Scaling Strategies: The Art of Keeping Up
If you have more growth than you can handle, you may be facing an operational constraint. If you want to continue to scale, consider setting up a waitlist for your services.
If you see the crunch persisting well into the future, consider offloading the constraint to an external agency. In today’s age of remote work, the opportunity to leverage various external resources is massive.
For example, external SDRs (sales development reps) are an effective way to scale your sales team without the hassle of hiring and training. Remember, the constraint needs to be relieved. Get it out of the way and move on to the next constraint. You can come back when you’re better equipped to handle staffing challenges.
Consider streamlining your operations around the potential clients that represent the biggest opportunity for your business. To determine the best sources of new business, weigh the following factors: market size, acquisition costs, lifetime value, and service delivery costs.
Be okay with rejecting new business that isn’t a good fit. Be okay with refunding and parting with difficult clients.
80/20 Rule: “What 20% of our clients bring in 80% of the value to our business?”
Maximize In-House Productivity
For in-house operations, start by maximizing the productive capacity of your key employees. An employee is “key” when they can be entirely relied on for a segment of operations.
Make sure key-employee time is spent entirely on stuff they’re valued for – and find a way to displace other work. Consider assigning virtual assistants to them, leveraging freelancers, and/or transitioning them to a team leader/project manager role.
High-Yield Management Principles: A Quick Review
- The cost of bad hiring is monumental.
- Track records and previous performance matters.
- Great people are hard to find, so when you do find them, value them.
- Continually hire, train, test, and sort new people.
- Set expectations and make goals clear.
- Consistently acknowledge staff achievements and express appreciation.
- Consistently acknowledge failure, address mistakes, and re-clarify expectations.
- A business’s workplace culture should be entirely based on its goals.
Invest in Process
Process is an underutilized method of increasing value and productivity.
The benefits of investing in process:
1. Increased Efficiency
Process reduces cognitive load. Employees with a process to follow work faster and make less errors.
2. Analytical operations
Process transforms operations into an objective and testable entity that can be analyzed and iterated.
3. Business resilience
Process builds your business’s value by making you less dependent on specific employees.
4. Exit Title
Businesses that rely on process – as opposed to people – are more appealing and valuable to potential buyers.
Productive team members already have a process for getting work done. But it’s often a habituated process they’re not consciously aware of.
Subscribe to a good process creation software solution and give your staff access. Ask your team to specify their processes and give them time to figure things out. Scrutinize their work by testing its usefulness and asking questions.
Continually update and iterate the process as you learn new things, get feedback, and make mistakes. Over time, you will keep discovering ways to add value to your services, without increasing your operational burden.
A Format for Creating Process
After several iterations with process design, here’s the format I currently use
01. Paradigms
A process should start with a few powerful paradigms that orient the employee and draw focus towards what’s important.
02. Additional Resources
Include links to high-yield additional resources in case employees require a knowledge refresher.
03. Process Items
Proceed through each step of the process item by item. Keep the core process simple and add additional information as an aside.
04. Checklists
End the process with a checklist to ensure nothing important is missed.
Processes are not courses and/or learning material. I’ve seen this mistake quite a few times. Processes are tools business use to optimize service delivery. They’re designed to be utilized by those with the requisite knowledge to do the job. Don’t teach. If the employee needs training, that is a completely separate issue.
4 Ideas For Market Expansion
Your target market’s demands and desires are a natural resource. Your business taps into this resource – and channels it for profit. As your business grows, it’ll become increasingly constrained by the limits of this resource.
To identify market constraints, monitor your business’s trajectory. You may be experiencing a market constraint if your business is well optimized and you’re hitting a growth ceiling. Stalled growth often comes in the form of dramatically increasing customer acquisition costs as you scale.
The 4 Categories of Market Expansion
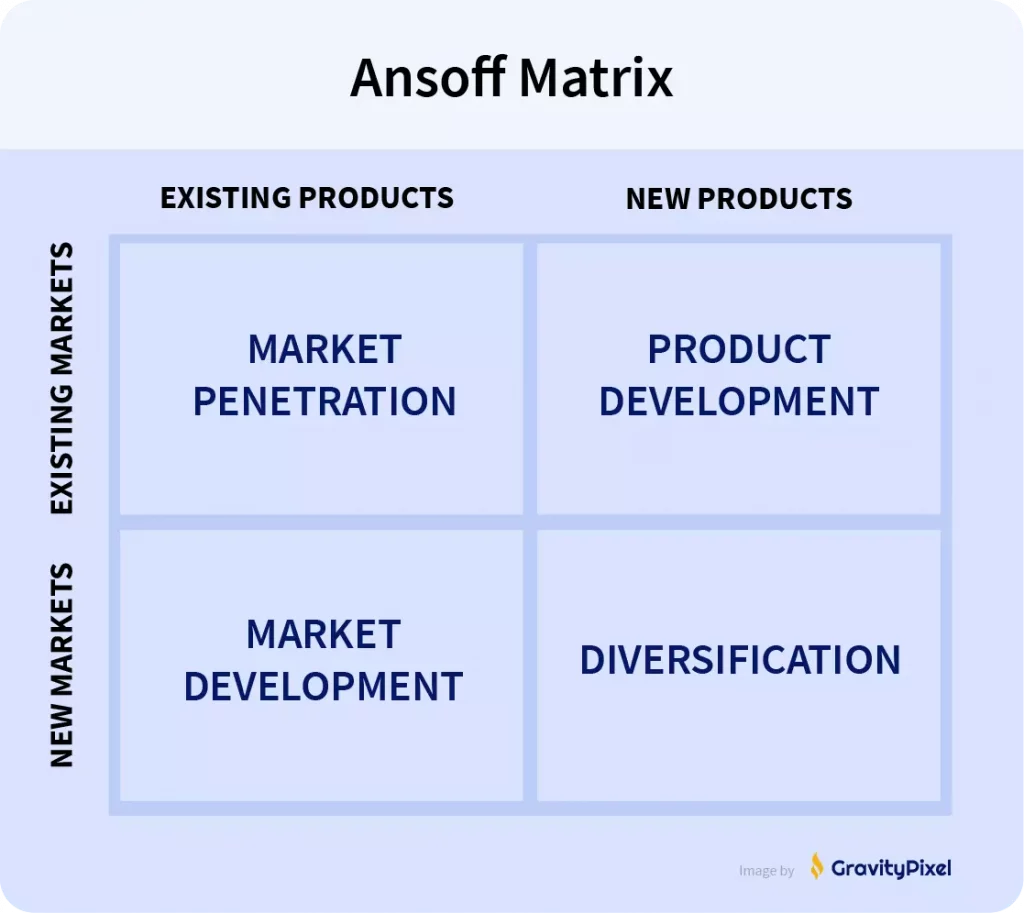
This diagram is called the “Ansoff Matrix,” It’s a popular framework for conceptualizing 4 types of market expansion.
- Market penetration: neither new product or new market
- Market development: expanding into a new market
- Product development: creating a new product
- Diversification: both new product and new market
What does and doesn’t count as a “new” market and “new” product is debatable, so don’t get too hung up on this. I’ll discuss one high-yield strategy for each of the four categories
1. Market Penetration
Increasing market penetration is a matter of accessing more of your current market. The more you can pay to acquire a customer, the more you can scale your customer acquisition. So increasing your customer lifetime value is a powerful market penetration strategy.
Another market penetration strategy involves increasing the cost-effectiveness of your marketing. This is best accomplished by enhancing your digital advertising.
5 Methods to Increase Your Digital Advertising ROI
1. Establish the fundamentals
Even if you’re running ads to a landing page, customers have a tendency to look a business up after seeing their ads. So a respectable online presence will significantly enhance your advertising efforts. Develop a high-performance website with valuable content, quality design, and integrated branding to generate trust and increase the perception of value.
2. Try display ads
All markets can be divided into “searchers” and “browsers.” Display ads target the “browser” – those individuals that may want your product, but won’t become customers until they’re hooked by an ad. Successful display ad campaigns have been known to generate very high ROIs.
3. Invest in e-mail follow-up
Some prospects won’t become customers until the 20th or 30th email. So develop an email follow-up chain that continues to nurture prospects for as long as possible.
4. Create custom audiences
Campaign data can be fed back into a campaign via custom audiences to boost its ROI.
5. Use retargeting
You can develop follow-up campaign ideas that target prospects based on their engagement with your campaign.
2. Product Expansion
Product expansion involves developing a new product/service for your current market. Often, the best opportunity for a new product is in improving on a popular offer. Try to develop a new mechanism that either removes a current limitation or increases the desired benefit.
Example: “Pain-free dentistry” is an example of product expansion via a new mechanism: It takes a high-demand service (dentistry) and removes an unpopular limitation of that service (pain).
While developing your product, seek feedback from your customer avatar. Shadow testing is a well known product expansion strategy that could save you the expenses and grief of creating a product that nobody wants. Shadow testing involves marketing your product/service to gauge response, before actually building it out.
3. Market Development
For the most part, if you’re expanding into a new market with the same product/service, you’re conducting a geographic expansion. For example, a local business opening a new physical location in a different city.
Here is a simple market development strategy:
- Theorize which market factors have made your current offer successful.
- Identify markets with similarities to these factors.
- Conduct market analysis.
- Choose the healthiest and most similar market.
4. Diversification
Many people argue that diversification is riskier than the other 3 categories. This isn’t necessarily true. A diversification idea can be very low risk if the company can execute it with little effort.
For example, it probably isn’t very risky for a personal tax accountant to begin offering business bookkeeping services.
That said, diversification is more challenging because you’re testing two variables at once. This can make strategic planning difficult because it’s more difficult to pinpoint constraints.
A good diversification strategy is to enter a growing market. Ideally, you should also pick something with the least operational strain.
For example, a home renovation company evaluates three growing contracting markets: aging in place, asbestos abatement, and smart homes. Since many of their previous clientele were elderly, they regularly asked for adaptations like widened doorways and grab bars. This made diversifying into the “aging in place” market an obvious choice.